It shouldn’t surprise me after all this time, but it does.
I’ve conducted around 30 interviews in two different organisations in the last couple of months, as part of some KM strategy work. The answers to the question: “what does knowledge management mean to you?” are often so varied, and usually include just one or two components or approaches . People have such different perspectives on what knowledge management is – and it’s rare for anyone to connect the different components together in any kind of holistic framework. “It’s about how we get the right knowledge to the right person at the right time. Oh and it’s to do with networks and conversations too.”
To be fair, knowledge management has been poorly defined and communicated in the external world, so it’s little wonder that people in organisations often approach it like the blind men and the elephant – each sensing a part, but not the whole, and drawing their own conclusions.
Here’s a holistic model for knowledge management. It isn’t new (it’s based on the model from BP in Learning to Fly)- but it’s still relevant and current today and does a good job of plotting a route through the KM landscape. Let me build it up for you.
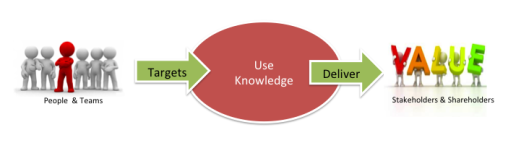
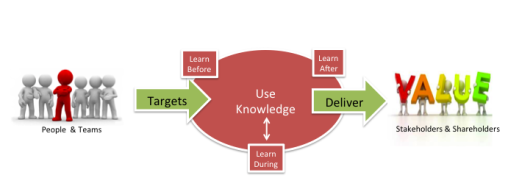
Start with the day-to-day matter of performance management and project management, where people and teams agree to goals and targets in order to deliver value which generally takes the form of profits for shareholders – or value for stakeholders.
How do they do this? By using and developing knowledge – their own expertise, knowledge from the team, elsewhere in the organisation, from professional advisors or others outside the organisation.
It’s a given that KM needs to connect directly to the goals and objectives of the organisation. So how does knowledge management improve, or accelerate the way in which they are achieved?
Firstly, through the application of learning. Learning before, during and after activities.
Without learning, we end up recycling old knowledge and documents – trapped between “connect and collect”, but not creating anything new.
- Learning before: how do we know that we’ve tapped into what the organisation already knows, and can we make sense of what it is knowing today?
- Learning after: how good are we at really learning and applying lessons from stories of personal experience?
- Learning during: do we have a culture of continuous learning, reviewing and improving?
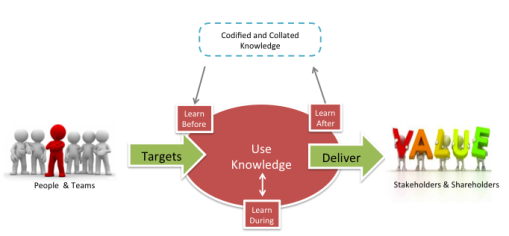
With processes for learning before and after in place, it’s important to manage the outputs of those processes – and to continue to refine, collate and curate a living, evolving, media-rich “knowledge bank”, from which withdrawals and deposits can be made.
…but of course, the capture knowledge is just a shadow of the knowledge which will always remain in the heads of individual experts, and within networks of people with questions, answers, experience and ideas. The reserves in this human knowledge bank are far greater.
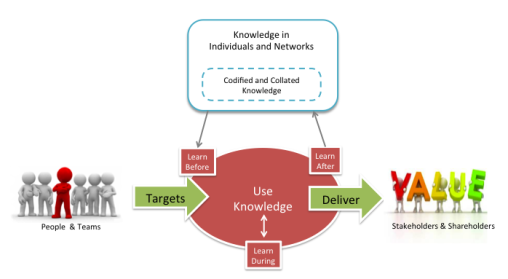
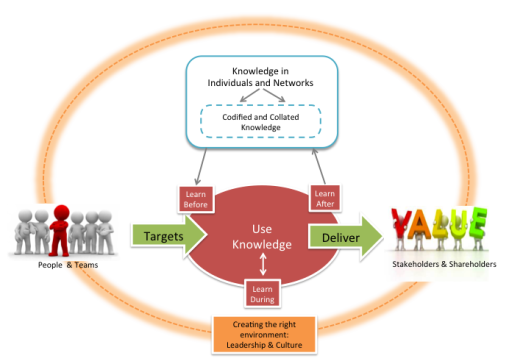
These networks and experts play a vital role in collating and curating knowledge on behalf of the organisation. They have the current awareness and they understand the most pressing business issues. Who better to steward the knowledge than an emergent community of subject matter experts and practitioners?
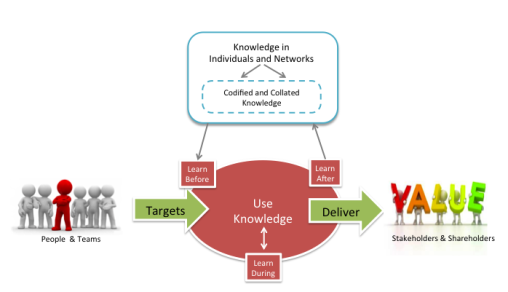 So now we’ve connected performance and project management with learning, learning with codification, and codification with networks, experience and expertise. The final part of the model recognises the role that culture and leadership behaviours and actions play to sustain an environment where these processes can thrive and interconnect.
So now we’ve connected performance and project management with learning, learning with codification, and codification with networks, experience and expertise. The final part of the model recognises the role that culture and leadership behaviours and actions play to sustain an environment where these processes can thrive and interconnect.
What motivates people to make the time to learn, connect and collate knowledge such that the value and efficiencies have a chance to flow through and create the stories to inspire others? How can leaders reinforce and role-model this?
It can take a little time to give birth to this kind of a supportive culture – but then again, elephants to have the longest gestation period of any mammal, so we shouldn’t be surprised.
Leave a comment